As the world continues to grapple with the challenges of infectious diseases, a growing concern has emerged in the form of polio vaccination hesitancy. Despite the remarkable success of vaccination campaigns in reducing the incidence of polio worldwide, a significant number of individuals are now expressing doubts and fears about the safety and efficacy of polio vaccines. This trend is not only limited to developing countries but has also been observed in developed nations, where vaccine hesitancy has become a major public health concern.
In this article, we will delve into the reasons behind polio vaccination hesitancy, explore the risks associated with not vaccinating against polio, and discuss strategies to address concerns and promote vaccination uptake.
History of Polio Vaccination
Polio, also known as poliomyelitis, is a highly infectious disease caused by the poliovirus. The disease can lead to paralysis, disability, and even death. In the early 20th century, polio outbreaks were common, and the disease was a major public health concern. The introduction of inactivated poliovirus vaccine (IPV) in the 1950s and oral poliovirus vaccine (OPV) in the 1960s marked a significant turning point in the fight against polio.
Through sustained vaccination efforts, the number of polio cases declined dramatically, and the disease was eventually eliminated in many parts of the world. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the number of polio cases decreased by over 99% since the launch of global eradication efforts in 1988.
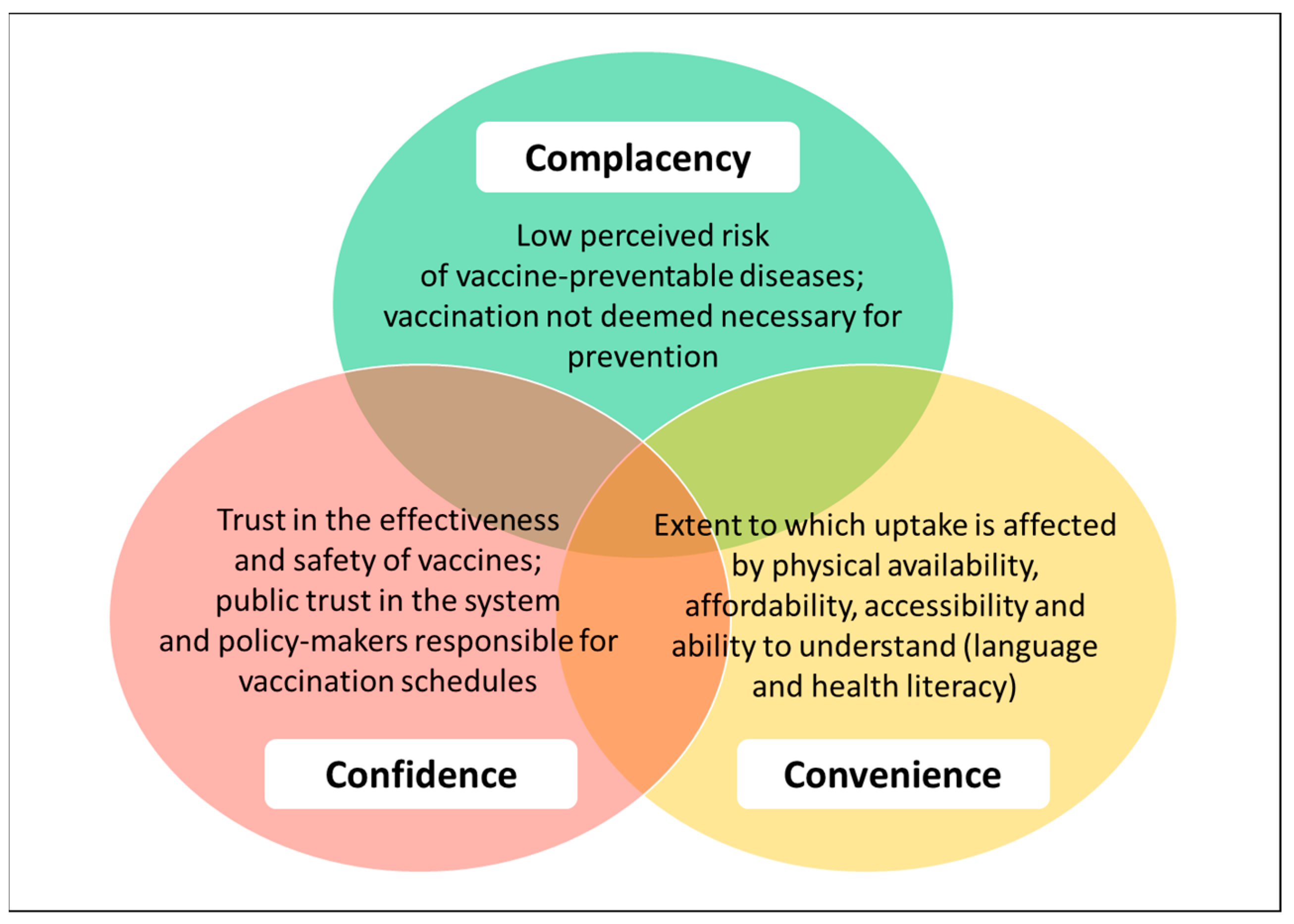
Reasons Behind Polio Vaccination Hesitancy
So, why are people hesitant to vaccinate against polio? The reasons are complex and multifaceted. Some of the common concerns include:
- Safety concerns: Some individuals believe that polio vaccines are not safe and can cause adverse reactions, such as allergic reactions or even paralysis.
- Efficacy concerns: Others question the effectiveness of polio vaccines in preventing the disease.
- Lack of awareness: In some communities, there is a lack of understanding about the risks of polio and the benefits of vaccination.
- Misinformation: Social media and other online platforms have contributed to the spread of misinformation about polio vaccines, fueling concerns and doubts.
- Cultural and religious beliefs: In some cultures, there may be myths or misconceptions about vaccines, leading to hesitancy.
- Trust issues: Mistrust of healthcare providers, governments, or pharmaceutical companies can also contribute to vaccination hesitancy.
Risks Associated with Not Vaccinating Against Polio
The risks of not vaccinating against polio are significant. Polio is a highly infectious disease that can spread quickly, especially in areas with poor sanitation and hygiene. If polio vaccination rates decline, the disease can staged a comeback, leading to outbreaks and epidemics.
Some of the risks associated with not vaccinating against polio include:
- Paralysis and disability: Polio can cause permanent paralysis and disability, which can have a significant impact on an individual’s quality of life.
- Death: In severe cases, polio can be fatal, especially in young children and individuals with compromised immune systems.
- Outbreaks and epidemics: Low vaccination rates can lead to outbreaks and epidemics, which can spread quickly and affect large numbers of people.
- Economic burden: Polio outbreaks can also have a significant economic burden, as they require significant resources to respond to and control.
Strategies to Address Concerns and Promote Vaccination Uptake
To address concerns and promote vaccination uptake, the following strategies can be employed:
- Education and awareness: Educating communities about the risks of polio and the benefits of vaccination can help address misconceptions and fears.
- Addressing safety concerns: Providing accurate information about the safety of polio vaccines and addressing concerns about adverse reactions can help alleviate fears.
- Building trust: Building trust with healthcare providers, governments, and pharmaceutical companies is critical to promoting vaccination uptake.
- Community engagement: Engaging with communities and involving them in vaccination efforts can help increase vaccination rates and promote acceptance.
- Social media campaigns: Utilizing social media platforms to promote accurate information about polio vaccines and address misinformation can help counteract negative messaging.
FAQs
- Is the polio vaccine safe?
Yes, the polio vaccine is safe and has been extensively tested for safety and efficacy. - Can the polio vaccine cause paralysis?
No, the polio vaccine cannot cause paralysis. While there is a small risk of adverse reactions, such as allergic reactions, paralysis is not a known side effect of the vaccine. - How effective is the polio vaccine?
The polio vaccine is highly effective in preventing polio, with a success rate of over 99%. - Do I need to get vaccinated against polio if I’ve already had the disease?
Yes, even if you’ve already had polio, it’s still important to get vaccinated to protect against future infections. - Can I get polio from the vaccine?
No, you cannot get polio from the vaccine. The vaccine contains inactivated or weakened virus, which cannot cause the disease.
Conclusion
Polio vaccination hesitancy is a growing concern that poses significant risks to public health. It is essential to address concerns and promote vaccination uptake to prevent the resurgence of polio. By educating communities, addressing safety concerns, building trust, and engaging with communities, we can promote acceptance and increase vaccination rates.
As we move forward in 2025, it is crucial that we continue to prioritize polio vaccination efforts and work together to eliminate this debilitating disease. We must also recognize the importance of vaccine hesitancy as a public health concern and take proactive steps to address it.
Ultimately, vaccination is a collective responsibility, and it requires the participation and commitment of individuals, communities, and governments. By working together, we can ensure that polio is eradicated and that future generations are protected against this devastating disease.
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Resurgence of Polio Vaccination Hesitancy: Understanding the Risks and Addressing Concerns. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!