The Science Behind the Chill:
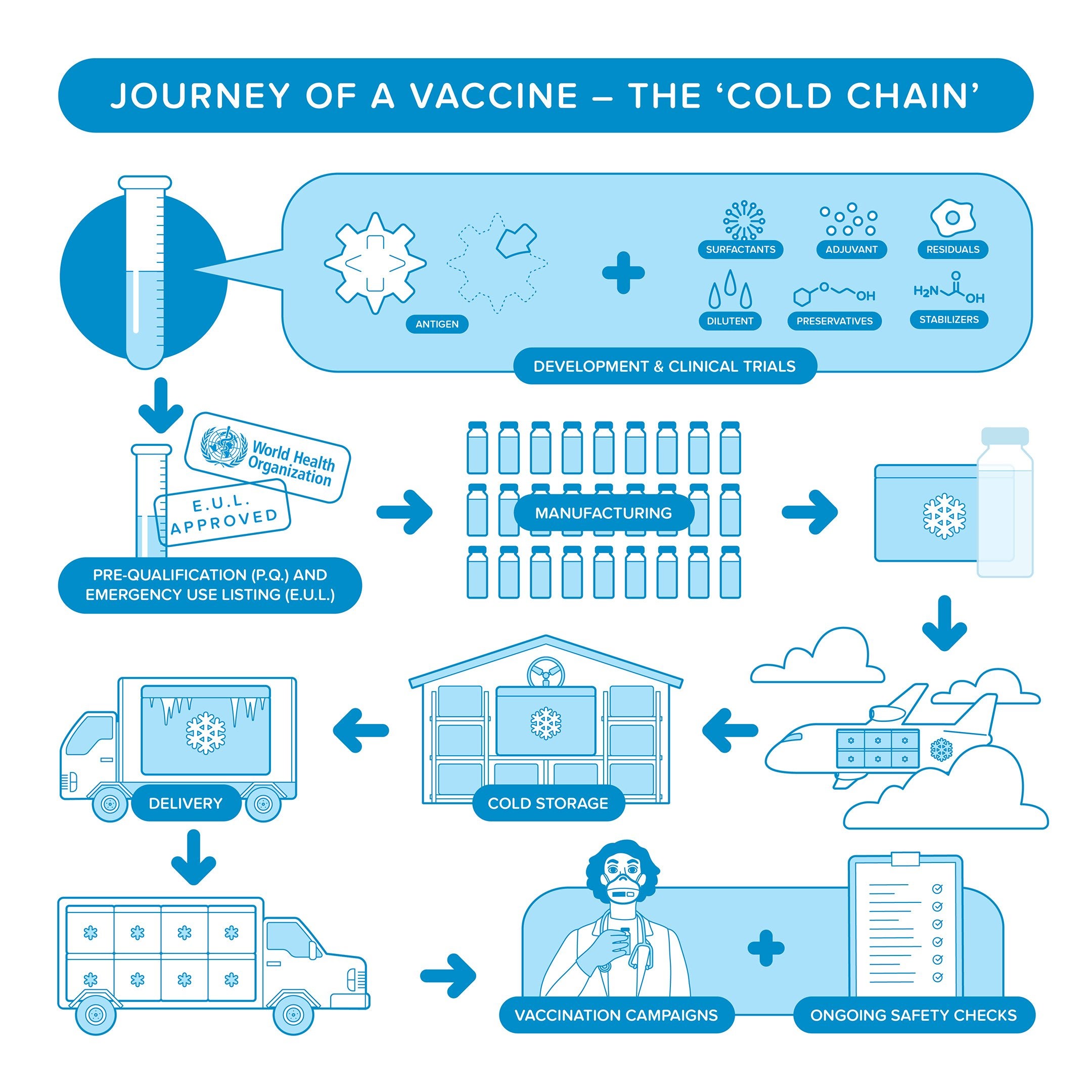
Vaccines are biological products, highly susceptible to degradation at warm temperatures.
Proteins within the vaccines, crucial for triggering an immune response, can denature and lose their functionality, rendering the vaccine useless. Each vaccine requires specific temperature ranges for storage and transportation to remain potent and safe.
The Cold Chain Ecosystem:
The cold chain is a temperature-controlled network encompassing every step involved in vaccine handling, from production facilities to vaccination points.
It involves a complex interplay of:
Manufacturing: Vaccines are initially produced in sterile environments under strict temperature controls.
Storage Facilities: Designated warehouses and freezers equipped with sophisticated monitoring and control systems ensure vaccines remain at their required temperatures throughout storage.
Transportation: Specialized vehicles, such as refrigerated trucks and containers, equipped with continuous temperature monitoring and tracking technology, are crucial for safe and timely vaccine delivery.
Distribution Centers: These hubs act as intermediary points, sorting and distributing vaccines to various healthcare facilities.
Healthcare Facilities: Hospitals, clinics, and vaccination centers must maintain cold storage facilities and ensure proper handling of vaccines during administration.
Challenges in Cold Chain Management:
Maintaining a seamless and reliable cold chain poses numerous challenges:
Temperature Fluctuations: Even slight deviations from the ideal temperature can compromise vaccine efficacy.
Power Outages: Loss of power can lead to rapid temperature increases, jeopardizing vaccine integrity.
Equipment Malfunction: Refrigerators and freezers can malfunction, requiring immediate attention and backup solutions.
Limited Infrastructure: Developing countries often lack adequate cold storage facilities and transportation infrastructure, hindering vaccine accessibility.
Human Error: Improper handling, temperature recording, and documentation can introduce vulnerabilities in the chain.
Technological Innovations:
Technological advancements are playing a vital role in strengthening cold chain logistics:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Temperature sensors and data loggers provide continuous tracking of vaccine temperatures throughout the supply chain.
- Cloud-Based Platforms: Data analytics and cloud-based platforms enable real-time monitoring, alerts, and improved decision-making.
- Passive Temperature-Controlled Packaging: Insulated packaging with integrated cooling agents can maintain vaccine temperatures for extended periods even without power.
- Mobile Refrigerators: Solar-powered and battery-operated refrigerated units extend vaccine accessibility to remote areas with limited infrastructure.
- Smart Vaccine Inventory Management Systems: Automated systems streamline inventory tracking, order fulfillment, and stock management, reducing wastage and improving efficiency.
Global Collaboration and Vaccine Equity:
Ensuring equitable access to vaccines requires global collaboration and concerted efforts to strengthen cold chain capabilities in all countries. Initiatives like the Global Vaccine Alliance (GAVI) and the World Health Organization (WHO) are instrumental in providing technical assistance, funding, and infrastructure support to developing countries.
Protecting Lives Through Resilient Cold Chain Logistics:
The cold chain is not just a logistical process; it’s a lifeline that protects countless lives. Robust cold chain management ensures vaccine efficacy, safeguards public health, and contributes to global disease eradication efforts.
Investing in technology, infrastructure, and capacity building is essential to building a resilient cold chain that can deliver life-saving vaccines to every corner of the world.
FAQ:
- Q: What are the most important factors to consider when designing a cold chain for vaccines?
A: The most crucial factors are maintaining strict temperature controls throughout the supply chain, ensuring uninterrupted power supply, using appropriate packaging and transportation equipment, and incorporating robust monitoring and tracking systems.
- Q: How can countries with limited resources strengthen their cold chains?
- A: Establishing partnerships with international organizations, prioritizing capacity building and training for cold chain personnel, leveraging technological innovations like passive cold chain packaging, and focusing on regional vaccine distribution centers can help.
- Q: What are the potential consequences of vaccine temperature deviations?
- A: Vaccine efficacy may be compromised, leading to reduced immunity and increased risk of disease outbreaks. In extreme cases, vaccines may become completely unusable.
Conclusion:
Cold chain logistics is an essential pillar of global health security, ensuring the safe and effective distribution of vaccines. Continuously strengthening cold chain infrastructure, leveraging technological advancements, and fostering global collaboration are crucial for protecting populations from vaccine-preventable diseases and building a healthier future for all.
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Cold chain logistics for vaccines. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!