What are Social Determinants of Health?
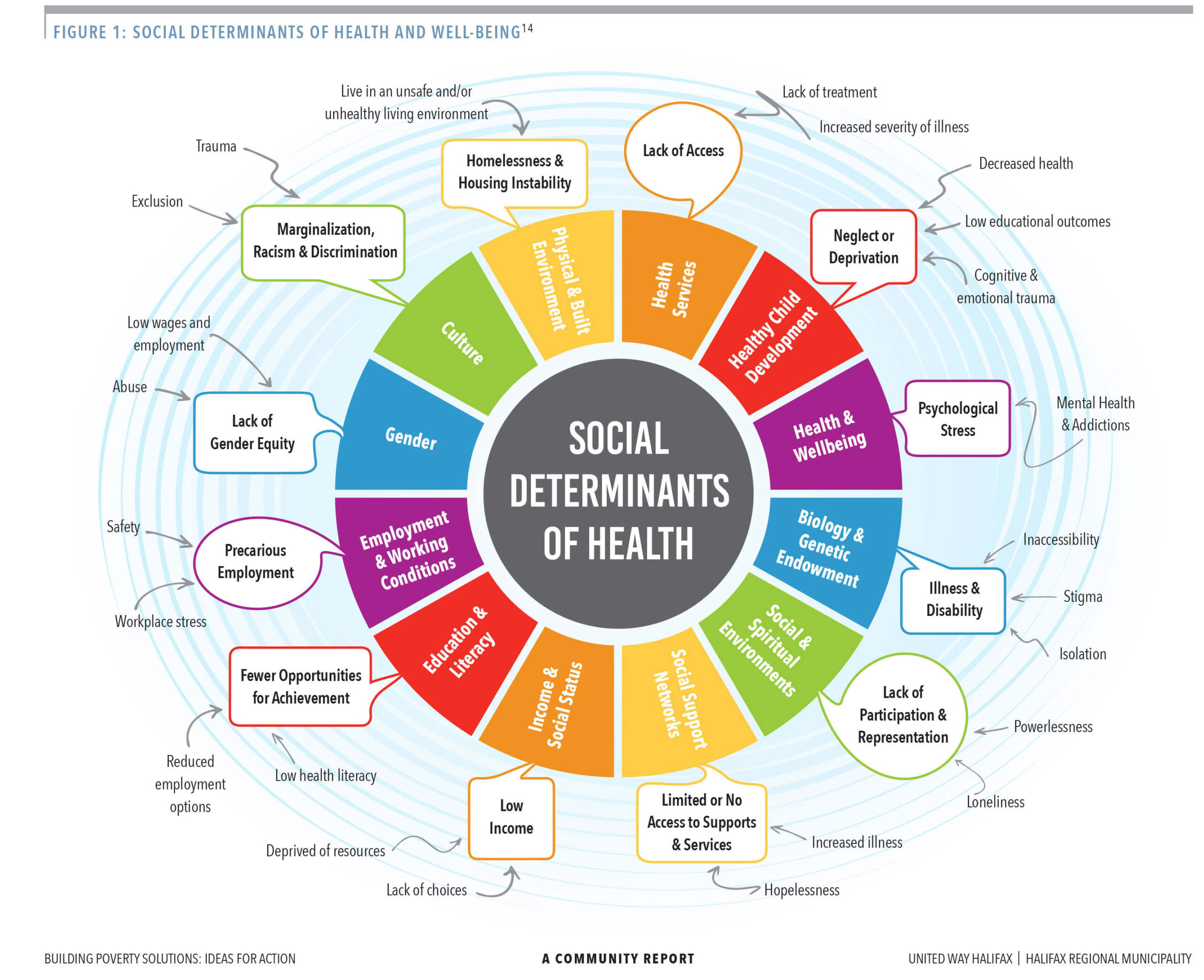
Social determinants of health refer to the socioeconomic and environmental factors that influence health outcomes. These factors can be broadly categorized into two groups: upstream and downstream determinants. Upstream determinants include factors such as socioeconomic status, education, occupation, and housing, which shape the social and economic context in which individuals live. Downstream determinants, on the other hand, include factors such as access to healthcare services, healthcare quality, and health behaviors, which are influenced by the upstream determinants.
Examples of Social Determinants of Health
Some examples of social determinants of health include:
- Income and Socioeconomic Status: Individuals with lower incomes and socioeconomic status are more likely to experience poor health outcomes, including higher rates of chronic disease, mental health problems, and mortality.
- Education: Higher levels of education are associated with better health outcomes, including lower rates of smoking, obesity, and mortality.
- Housing and Environment: Poor housing conditions, such as overcrowding, poor ventilation, and lack of access to green spaces, can contribute to poor health outcomes, including respiratory problems, mental health issues, and injuries.
- Occupation and Employment: Certain occupations, such as those that involve exposure to hazardous substances or long working hours, can increase the risk of poor health outcomes.
- Access to Healthcare Services: Individuals who lack access to healthcare services, including health insurance, primary care, and specialty care, are more likely to experience poor health outcomes.
The Impact of Social Determinants of Health
The impact of social determinants of health on wellbeing is significant. Research has shown that:
- Health Inequalities: Social determinants of health contribute to health inequalities, with disadvantaged groups experiencing poorer health outcomes and lower life expectancy.
- Mortality Rates: Social determinants of health, such as income and education, are associated with mortality rates, with lower socioeconomic groups experiencing higher mortality rates.
- Chronic Disease: Social determinants of health, such as housing and environment, can contribute to the development of chronic diseases, such as diabetes, heart disease, and respiratory problems.
- Mental Health: Social determinants of health, such as socioeconomic status and occupation, can contribute to mental health problems, including depression, anxiety, and stress.
Addressing Social Determinants of Health
Addressing social determinants of health requires a multi-faceted approach that involves policy, practice, and community engagement. Some strategies for addressing social determinants of health include:
- Healthcare Policy: Implementing healthcare policies that address social determinants of health, such as increasing access to healthcare services, improving healthcare quality, and addressing health inequalities.
- Community-Based Initiatives: Implementing community-based initiatives that address social determinants of health, such as housing, education, and employment programs.
- Health Education: Providing health education and promoting health literacy to empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health.
- Intersectoral Collaboration: Collaborating across sectors, including healthcare, education, and social services, to address social determinants of health.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What are the most important social determinants of health?
The most important social determinants of health include income and socioeconomic status, education, housing and environment, occupation and employment, and access to healthcare services. - How do social determinants of health affect mental health?
Social determinants of health, such as socioeconomic status and occupation, can contribute to mental health problems, including depression, anxiety, and stress. - Can social determinants of health be changed?
Yes, social determinants of health can be changed through policy, practice, and community engagement. - What is the role of healthcare providers in addressing social determinants of health?
Healthcare providers play a critical role in addressing social determinants of health by providing health education, promoting health literacy, and referring patients to community-based resources. - How can individuals address social determinants of health in their own lives?
Individuals can address social determinants of health in their own lives by seeking out health education and resources, engaging in health-promoting behaviors, and advocating for policies and programs that address social determinants of health.
Conclusion
The social determinants of health play a crucial role in shaping health outcomes. Addressing these determinants requires a multi-faceted approach that involves policy, practice, and community engagement. By understanding the impact of social determinants of health on wellbeing, we can work to create healthier and more equitable communities. As healthcare providers, policymakers, and individuals, we must prioritize addressing social determinants of health to improve health outcomes and reduce health inequalities. Ultimately, addressing social determinants of health is essential for achieving the WHO’s definition of health and promoting overall wellbeing.
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Social determinants of health. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!