Introduction to Infectious Diseases
Infectious diseases are illnesses caused by the invasion of a host organism by a pathogen, such as a bacterium, virus, fungus, or parasite. These diseases can be spread through various means, including person-to-person contact, contaminated food and water, and vectors such as insects and animals. Infectious diseases can range from mild to severe, and some can be life-threatening if left untreated.
Importance of Infectious Disease Control
Infectious disease control is essential for several reasons:
- Prevention of morbidity and mortality: Infectious diseases can cause significant illness and death, especially in vulnerable populations such as the elderly, young children, and people with weakened immune systems.
- Protection of public health: Infectious diseases can spread quickly and widely, posing a significant threat to public health. Controlling infectious diseases helps to prevent outbreaks and epidemics.
- Economic benefits: Infectious diseases can have significant economic impacts, including lost productivity, healthcare costs, and damage to trade and tourism.
- Social benefits: Infectious disease control can help to reduce social disruption, including school closures, travel restrictions, and community lockdowns.
Methods of Infectious Disease Control
There are several methods of controlling infectious diseases, including:
- Vaccination: Vaccination is one of the most effective methods of preventing infectious diseases. Vaccines work by stimulating the body’s immune system to produce antibodies that can recognize and fight specific pathogens.
- Antimicrobial therapy: Antimicrobial therapy, including antibiotics and antiviral medications, can be used to treat infectious diseases caused by bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens.
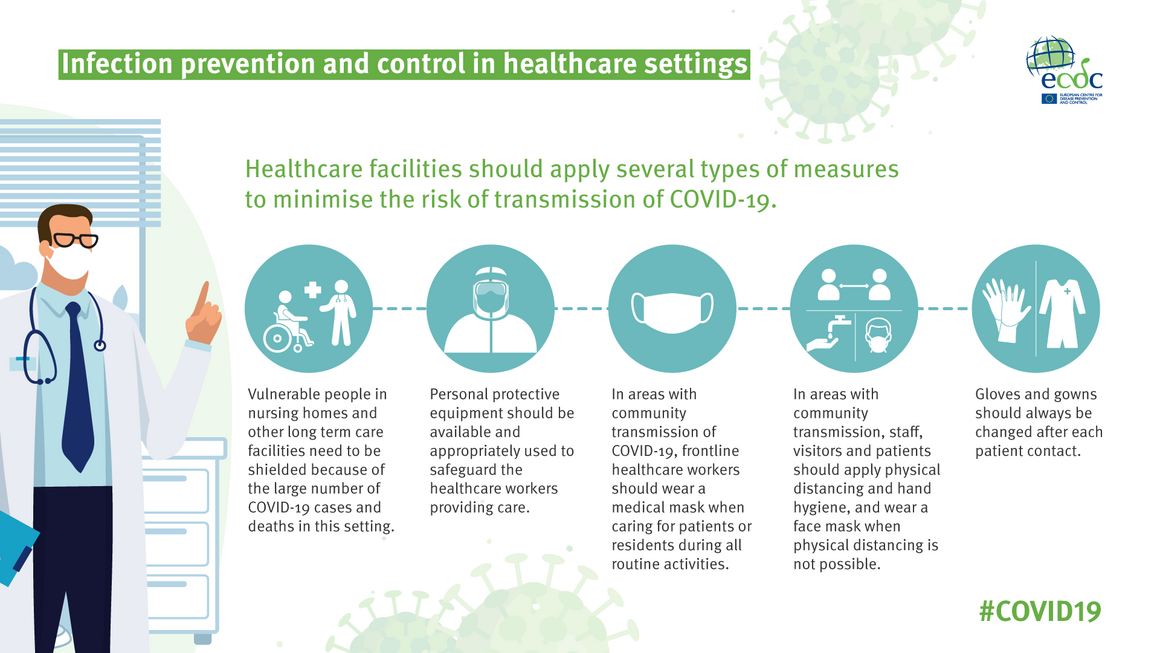
- Infection control practices: Infection control practices, such as hand hygiene, personal protective equipment (PPE), and sterilization of medical equipment, can help to prevent the spread of infectious diseases in healthcare settings.
- Surveillance and outbreak response: Surveillance and outbreak response involve monitoring for infectious disease outbreaks and responding quickly to prevent further spread.
- Vector control: Vector control, including the use of insecticides and bed nets, can help to prevent the spread of infectious diseases such as malaria and Zika virus.
- Environmental health: Environmental health measures, including sanitation and hygiene, can help to prevent the spread of infectious diseases such as cholera and typhoid fever.
Challenges in Controlling Infectious Diseases
Despite the importance of infectious disease control, there are several challenges that must be addressed, including:
- Antimicrobial resistance: The overuse and misuse of antimicrobial medications have led to the development of antimicrobial resistance, making it more difficult to treat infectious diseases.
- Emerging and re-emerging diseases: New and re-emerging diseases, such as COVID-19 and Ebola, can pose significant challenges to infectious disease control.
- Globalization and travel: Globalization and travel have increased the risk of infectious disease spread, as people can now travel quickly and easily across the globe.
- Climate change: Climate change can increase the risk of infectious disease spread, as changing weather patterns and temperatures can facilitate the spread of disease vectors such as mosquitoes and ticks.
- Health disparities: Health disparities, including lack of access to healthcare and poor living conditions, can increase the risk of infectious disease spread in vulnerable populations.
FAQs
- What is the most effective way to prevent infectious diseases?
The most effective way to prevent infectious diseases is through vaccination, which can provide immunity against specific pathogens. - How can I protect myself from infectious diseases?
You can protect yourself from infectious diseases by practicing good hygiene, including hand washing and proper use of PPE, and staying up-to-date on recommended vaccinations. - What is the role of antimicrobial therapy in controlling infectious diseases?
Antimicrobial therapy can be used to treat infectious diseases caused by bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens. However, the overuse and misuse of antimicrobial medications have led to the development of antimicrobial resistance. - How can I prevent the spread of infectious diseases in my community?
You can prevent the spread of infectious diseases in your community by practicing good hygiene, staying home when you are sick, and getting vaccinated against infectious diseases. - What is the role of government in controlling infectious diseases?
Government plays a critical role in controlling infectious diseases, including providing funding for research and development of new treatments and vaccines, implementing policies to prevent the spread of infectious diseases, and responding to outbreaks and epidemics.
Conclusion
Infectious disease control is a critical aspect of public health, and it requires a multidisciplinary approach that involves healthcare professionals, policymakers, and the general public. The control of infectious diseases involves several methods, including vaccination, antimicrobial therapy, infection control practices, surveillance and outbreak response, vector control, and environmental health. Despite the challenges faced in controlling infectious diseases, including antimicrobial resistance, emerging and re-emerging diseases, globalization and travel, climate change, and health disparities, it is possible to prevent and control infectious diseases through a concerted effort. By understanding the importance of infectious disease control and taking steps to prevent the spread of infectious diseases, we can protect ourselves, our communities, and the world from the threat of infectious diseases.
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Infectious disease control. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!